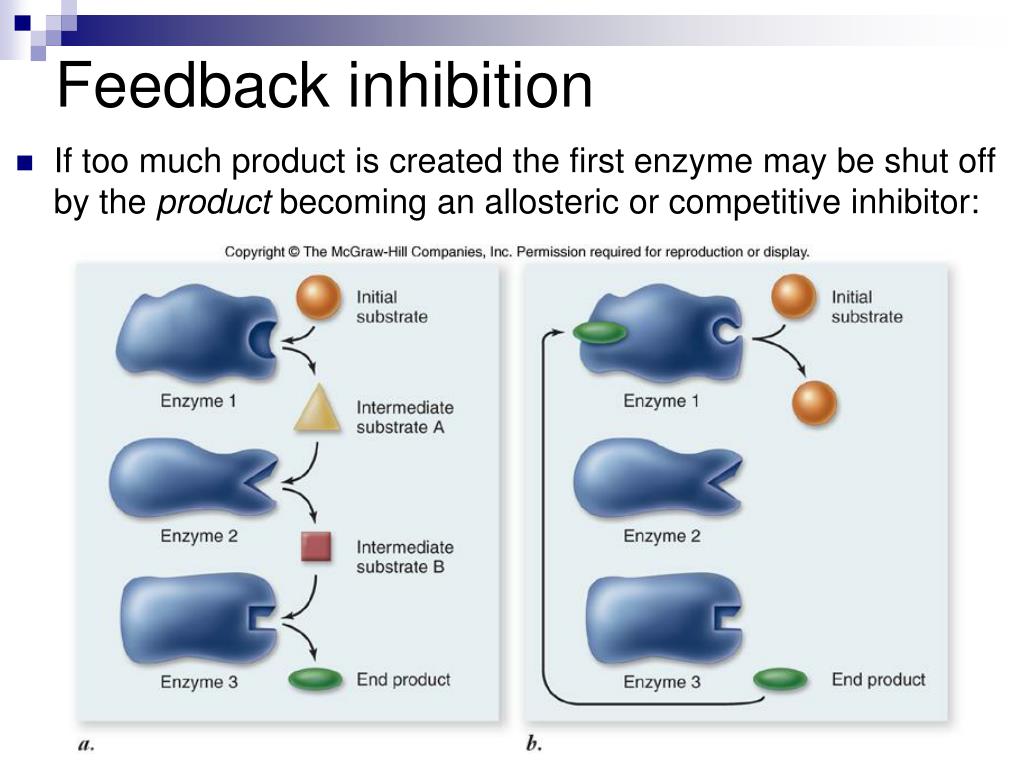
Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways . in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important.
from www.slideserve.com
in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important.
PPT Energy, Enzymes, and Biological Reactions PowerPoint Presentation
Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2683737 Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: the higher the concentration of the final product,. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.pinterest.com
Khan Academy Cellular respiration, Photosynthesis and cellular Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. feedback inhibition, where the end product. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.youtube.com
Feedback Inhibition of Biochemical Pathways. YouTube Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From biologydictionary.net
Origins of Cell Compartmentalization AP Biology Biology Dictionary Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. A) the substrate. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From slideplayer.com
Energy and Metabolism Chapter ppt download Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2683737 Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. producing both amino acids and nucleotides. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.researchgate.net
Cholesterol biosynthesis pathway and its feedback mechanism Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.scienceabc.com
Feedback Inhibition Definition, Example And A Brief Explanation Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From jackwestin.com
Feedback Regulation Control Of Enzyme Activity MCAT Content Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4283724 Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. in feedback inhibition, the. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.macmillanhighered.com
hillis2e_ch03 Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.researchgate.net
Direct and indirect pathways of the basal ganglia. The direct pathway Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.britannica.com
Endproduct inhibition biochemistry Britannica Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. Additionally, atp is an allosteric. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 7.6 Enzymes (AHL) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2453618 Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. Additionally, atp is. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From opentextbc.ca
4.1 Energy and Metabolism Concepts of Biology1st Canadian Edition Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. Additionally, atp is an allosteric regulator. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: feedback. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.vecteezy.com
Scientific diagram illustrate the explanation and concept of metabolic Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. Additionally,. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.youtube.com
Feedback Inhibition or End Product Inhibition of Enzymes YouTube Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways the higher the concentration of the final product, the more likely that product will bind to the allosteric site of. producing both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically: feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.
From www.pinterest.com
allosteric activation / feedback inhibition Biochemistry, Cell Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways in feedback inhibition, the inhibitor of the biochemical pathway is typically; feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in. A) the substrate of the enzyme inhibited. feedback inhibition, in enzymology, suppression of the activity of an enzyme, participating in a sequence of reactions by. the. Feedback Inhibition Of Biochemical Pathways.